Diabetic neuropathy, the hidden danger of nerve damage, is a condition that affects many women who have diabetes. This condition poses a significant risk as it can lead to the loss of sensation in various parts of the body. With this nerve damage, individuals may not be able to feel pain, temperature changes, or even injury. Understanding the complexities of diabetic neuropathy is crucial in order to prevent further complications and provide appropriate care. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this often overlooked yet critical aspect of diabetes management. Ready to uncover the hidden danger of diabetic neuropathy? Let’s dive in!
This image is property of media.springernature.com.
In This Article
ToggleWhat is Diabetic Neuropathy?
Diabetic neuropathy refers to nerve damage that occurs as a result of diabetes. It is a common complication of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, affecting millions of people worldwide. The condition occurs when high blood sugar levels over an extended period of time start to damage the nerves throughout the body. Diabetic neuropathy can be a hidden danger, as it often develops slowly and may go unnoticed until symptoms become severe. Understanding the different types, causes, and symptoms of diabetic neuropathy is essential for early detection and intervention.
Types of Diabetic Neuropathy
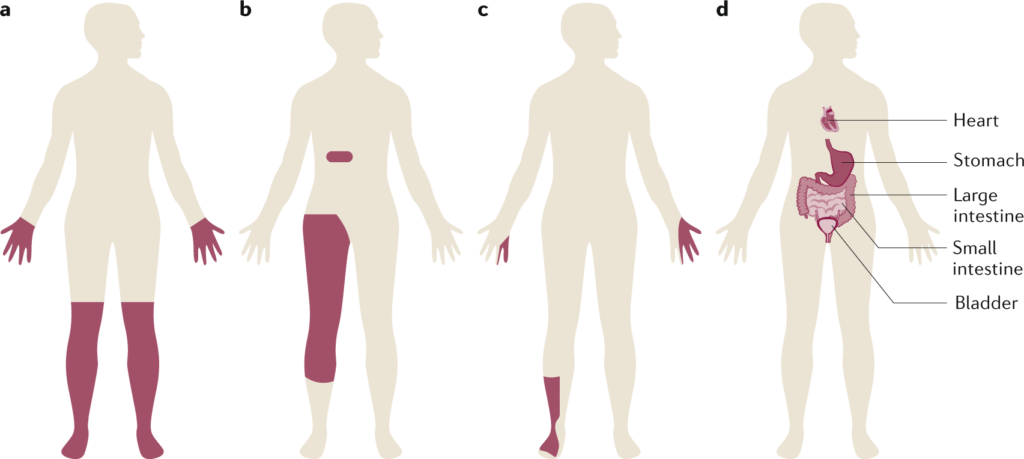
There are several types of diabetic neuropathy, each affecting different nerves in the body. Peripheral neuropathy is the most common form, affecting the peripheral nerves in the legs and feet. This can result in numbness, tingling, and pain in the extremities. Autonomic neuropathy affects the nerves that control involuntary bodily functions, leading to problems with digestion, heart rate, and blood pressure. Proximal neuropathy affects the nerves in the hips, thighs, and buttocks, causing weakness and pain. Focal neuropathy is the least common type, and it affects specific nerves, leading to sudden and severe pain in a particular area.
Causes of Diabetic Neuropathy
The primary cause of diabetic neuropathy is prolonged high blood sugar levels. When blood sugar levels are consistently elevated, it can lead to damage to the nerves throughout the body. Additionally, other factors such as smoking, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol can exacerbate the risk of developing diabetic neuropathy. Poorly controlled diabetes and a long duration of having diabetes also contribute to the development of this condition. Understanding these causes can help individuals with diabetes take proactive steps to prevent or manage diabetic neuropathy.
Symptoms of Diabetic Neuropathy
The symptoms of diabetic neuropathy vary depending on the type and extent of nerve damage. For peripheral neuropathy, common symptoms include numbness or reduced sensation in the hands, feet, or legs, tingling or burning sensations, sharp or shooting pains, and muscle weakness. Autonomic neuropathy may result in symptoms such as dizziness upon standing, difficulty swallowing, bladder problems, and sexual dysfunction. Proximal neuropathy typically causes pain in the hips, thighs, or buttocks, which can be severe. Focal neuropathy may cause sudden weakness or pain in a specific area, such as the head, torso, or leg.
Understanding Nerve Damage
How Diabetes Affects Nerves
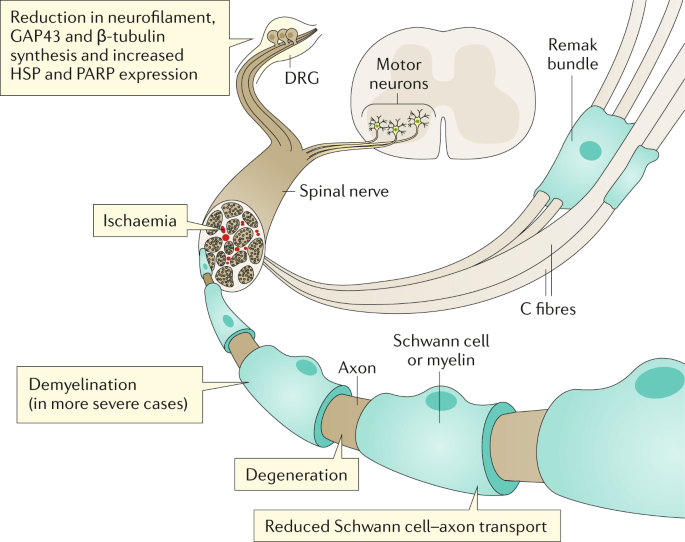
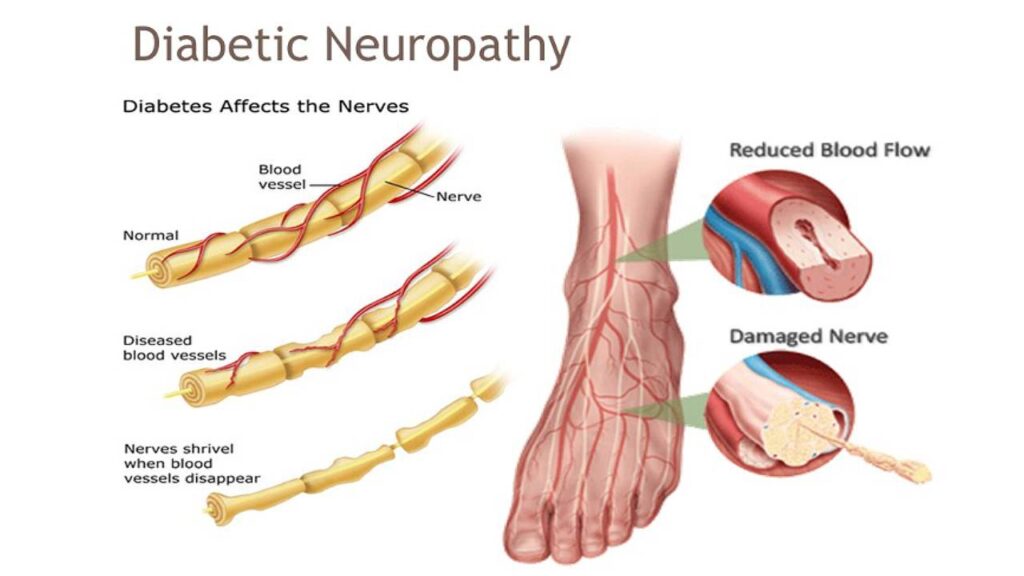
Diabetes can affect nerves in several ways. Firstly, high blood sugar levels can cause chemical changes in the nerves, leading to nerve damage. Secondly, diabetes can cause poor blood circulation, depriving the nerves of essential oxygen and nutrients, further contributing to nerve damage. Lastly, diabetes can also cause inflammation, which can damage the nerves directly or indirectly. It is important to understand the impact of diabetes on nerves to effectively prevent and manage diabetic neuropathy.
The Role of Glucose Control
Maintaining consistent and healthy blood sugar levels is crucial in preventing or minimizing diabetic neuropathy. High blood sugar levels over an extended period of time can cause damage to the nerves, leading to neuropathy. By monitoring blood sugar levels and following a proper diabetes management plan, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing diabetic neuropathy. Regular glucose monitoring, medication compliance, and lifestyle modifications all play a vital role in maintaining optimal glucose control.
Progression of Nerve Damage
Diabetic neuropathy typically progresses slowly and may worsen over time. Initially, individuals may experience mild symptoms such as tingling or numbness in the extremities. However, as the nerve damage progresses, the symptoms can become more severe and debilitating. It is essential to detect and intervene in the early stages of diabetic neuropathy to slow down or halt its progression. Regular check-ups and timely adjustments in treatment plans can help individuals effectively manage the progression of nerve damage.
The Hidden Danger
Loss of Sensation
One of the most significant dangers associated with diabetic neuropathy is the loss of sensation. Nerve damage in the extremities can lead to reduced or complete loss of feeling, making it difficult to detect injuries or wounds. Individuals may unknowingly develop blisters, sores, or cuts that can go unnoticed due to the lack of sensation. This loss of protective sensation puts individuals at a higher risk of developing complications, such as infections and ulcers.
Risk of Injuries and Infections
When individuals with diabetic neuropathy are unable to sense pain or discomfort, they are more susceptible to injuries and infections. Minor cuts or blisters can quickly escalate into serious infections, particularly in the feet. Additionally, individuals may unknowingly place excessive pressure on certain areas of their body or wear ill-fitting shoes, leading to injuries or calluses. The impaired ability to heal and fight off infections can further complicate these issues.
Delayed Healing
Diabetic neuropathy can also lead to delayed healing of wounds or injuries. Due to the compromised blood circulation and reduced nerve function, the body’s natural healing processes may be hindered. This delay in the healing process can increase the risk of infections and make it more challenging for individuals to recover from injuries or surgeries. It is crucial for individuals with diabetic neuropathy to prioritize proper wound care and seek medical attention promptly for any injuries.
Muscle Weakness and Balance Issues
In addition to sensory impairment, diabetic neuropathy can cause muscle weakness and balance issues. The nerves that control muscle movement and coordination may be affected, leading to difficulties in maintaining balance and performing everyday tasks. These physical limitations can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life and increase the risk of falls and injuries. Regular exercise and physical therapy can play a vital role in managing muscle weakness and improving balance.
Preventing Diabetic Neuropathy
Maintaining Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
One of the most effective ways to prevent or delay the onset of diabetic neuropathy is to maintain healthy blood sugar levels. By monitoring and controlling blood glucose through regular testing, medication adherence, and lifestyle modifications, individuals with diabetes can significantly reduce the risk of nerve damage. Consistent glucose control not only helps prevent neuropathy but also slows down its progression in those already affected.
Regular Exercise and Physical Activity
Engaging in regular exercise and physical activity is not just beneficial for overall health, but it also plays a crucial role in preventing diabetic neuropathy. Physical activity improves blood circulation, promotes nerve health, and helps maintain a healthy weight. Individuals should aim for a combination of aerobic exercises, strength training, and flexibility exercises, as recommended by their healthcare professional.
Healthy Diet and Weight Management
A healthy diet and weight management are essential components of preventing and managing diabetic neuropathy. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help regulate blood sugar levels and promote nerve health. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight reduces the strain on the body and improves overall health outcomes. It is recommended to consult with a registered dietitian or nutritionist for personalized dietary advice.
Foot Care and Regular Check-ups
Proper foot care and regular check-ups are crucial in preventing and managing the complications associated with diabetic neuropathy. Individuals should examine their feet regularly for any signs of injury, wear comfortable and properly fitting shoes, and avoid walking barefoot. Regular visits to a podiatrist and regular foot screenings by a healthcare professional are essential for early detection of any foot-related issues. Routine medical check-ups are also necessary to monitor nerve function and overall health.

This image is property of my.clevelandclinic.org.
Diagnosing Diabetic Neuropathy
Medical History and Physical Examination
Diagnosing diabetic neuropathy begins with a comprehensive evaluation of an individual’s medical history and a thorough physical examination. The healthcare professional will inquire about the symptoms experienced, their duration, and any other relevant medical conditions or risk factors. The physical examination will typically include tests to assess sensory function, muscle strength, reflexes, and coordination.
Neurological Tests
Neurological tests, such as the monofilament test or the tuning fork test, are often used to assess sensory function and detect any abnormalities. These tests involve applying light pressure or vibrations to specific areas to evaluate the individual’s ability to perceive touch or temperature changes accurately. Neurological tests provide important insights into the extent and nature of nerve damage.
Nerve Conduction Studies
Nerve conduction studies (NCS) measure the speed and strength of electrical signals along the nerves. Electrodes are placed on various points of the body, and a small electrical impulse is delivered to stimulate the nerves. The response is then recorded, and the data obtained can help identify any disruptions or abnormalities in nerve function. NCS is a valuable tool in diagnosing and evaluating the severity of diabetic neuropathy.
Electromyography (EMG)
Electromyography (EMG) is often performed in conjunction with NCS to assess the health and function of muscles and the nerves controlling them. During an EMG, thin needles are inserted into specific muscles to record their electrical activity at rest and during contraction. This procedure helps determine if muscle weakness is due to nerve damage and the extent of nerve involvement.
Skin Biopsy
In some cases, a skin biopsy may be recommended to evaluate small nerve fibers in the skin. A small sample of skin is extracted, typically from the leg, and examined under a microscope for signs of nerve damage or loss. Skin biopsies can provide valuable information about the severity and progression of diabetic neuropathy, particularly in cases where other diagnostic tests may be inconclusive.
Blood Tests
Blood tests may be conducted to assess blood sugar levels, cholesterol levels, kidney function, and other potential factors contributing to the development or progression of diabetic neuropathy. These tests help identify any underlying health issues and guide appropriate treatment strategies.
Managing Diabetic Neuropathy
Pain Management
Pain management is a critical aspect of diabetic neuropathy treatment. Depending on the severity and type of pain experienced, healthcare professionals may recommend over-the-counter or prescription pain medications. These may include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antidepressants, anticonvulsants, or opioids. However, it is important to work closely with a healthcare professional to find the most suitable pain management approach tailored to individual needs.
Medications
Various medications may be prescribed to manage different aspects of diabetic neuropathy. Antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), can help relieve pain and improve sleep quality. Anticonvulsants, like gabapentin or pregabalin, can help control nerve-related pain. Topical creams or patches containing lidocaine or capsaicin may also provide temporary relief from pain or discomfort.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a significant role in managing diabetic neuropathy symptoms and improving overall function. A physical therapist can create a customized exercise program focusing on strengthening weak muscles, improving balance, and increasing mobility. Physical therapy sessions may also include techniques such as manual therapy, massage, and stretching to alleviate pain and improve nerve function.
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) is a non-invasive therapy that uses a small battery-operated device to deliver low-level electrical impulses to the affected area. The electrical impulses help reduce pain by blocking the transmission of pain signals and promoting the release of endorphins, the body’s natural pain relievers. TENS units can be used at home under the guidance of a healthcare professional to manage chronic pain associated with diabetic neuropathy.
Nerve Decompression Surgery
In certain cases of severe nerve compression or entrapment, nerve decompression surgery may be recommended. This procedure involves relieving pressure on the affected nerve by removing surrounding tissues or structures causing compression. Nerve decompression surgery has shown promising results in reducing pain and improving nerve function in some individuals with diabetic neuropathy.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
Complementary and alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, biofeedback, and herbal supplements, may be considered as part of a multidisciplinary approach to managing diabetic neuropathy. These therapies are aimed at reducing pain, promoting relaxation, improving nerve function, and enhancing overall well-being. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating these therapies into the treatment plan to ensure their safety and effectiveness.
This image is property of media.springernature.com.
Living with Diabetic Neuropathy
Adapting to Sensory Loss
Living with sensory loss due to diabetic neuropathy can be challenging, but there are several strategies for adapting to these changes. Using alternative methods like visual inspection or regular foot checks with a mirror can help identify potential injuries or issues. Wearing protective footwear and properly fitting shoes can reduce the risk of foot injuries. Assistive devices, such as canes or grab bars, can also provide additional support and stability for individuals experiencing muscle weakness or balance issues.
Monitoring Foot Health
Regular foot care is essential for individuals with diabetic neuropathy to prevent complications such as ulcers and infections. Proper foot hygiene, including daily washing and thorough drying, is crucial. Regular inspection for any signs of injury, blisters, or calluses is necessary, and these should be addressed promptly. Moisturizing the feet and trimming toenails carefully can also help maintain foot health. Working closely with a podiatrist and following their recommendations for foot care is highly recommended.
Regular Medical Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups are vital for individuals with diabetic neuropathy to monitor their nerve function, overall health, and any potential complications. Routine tests, such as blood sugar levels, cholesterol levels, and kidney function tests, help ensure that diabetes is well-managed and any related conditions are promptly addressed. Regular visits to healthcare professionals allow for adjustments in treatment plans as needed and help prevent complications associated with diabetic neuropathy.
Emotional Support and Self-care
Living with diabetic neuropathy can have a significant impact on an individual’s emotional well-being. Coping with chronic pain, adapting to sensory loss, and managing the daily challenges can be overwhelming. Seeking emotional support from friends, family, or support groups can provide valuable encouragement and a sense of community. Engaging in self-care activities, such as relaxation techniques, hobbies, or pursuing interests, can also help individuals cope with the emotional aspects of living with diabetic neuropathy.
Preventing Complications
Preventing complications associated with diabetic neuropathy is paramount to leading a healthy and fulfilling life. By adhering to a comprehensive diabetes management plan, including glucose monitoring, healthy lifestyle choices, and regular medical check-ups, individuals can minimize the risk of developing ulcers, infections, or other health issues. Awareness of the body, prompt wound care, and vigilant foot hygiene can significantly reduce the chances of complications. It is important to seek immediate medical attention for any concerning symptoms or complications to prevent their escalation.
Complications of Diabetic Neuropathy
Ulcers and Infections
The loss of sensation and impaired healing associated with diabetic neuropathy can increase the risk of developing ulcers and infections, particularly in the feet. Minor injuries or pressure points may go unnoticed, leading to the development of non-healing ulcers that are susceptible to infection. Regular foot care, proper wound management, and prompt medical attention for any signs of infection are crucial in preventing the progression of ulcers and infections.
Amputations
In severe cases of diabetic neuropathy, the development of ulcers, infections, or non-healing wounds can lead to the need for amputation. The compromised blood flow, reduced sensation, and delayed healing make it challenging for wounds to heal properly, increasing the risk of tissue damage and infection. Maintaining optimal glucose control, regular foot care, and seeking medical attention at the earliest signs of foot complications can help prevent the need for amputations.
Autonomic Neuropathy
Autonomic neuropathy, a type of diabetic neuropathy affecting the nerves controlling involuntary bodily functions, can lead to various complications. These may include problems with digestion, such as gastroparesis (delayed stomach emptying), constipation, or diarrhea. Autonomic neuropathy can also affect the cardiovascular system, leading to fluctuations in heart rate and blood pressure. It is vital to manage autonomic neuropathy through medication, lifestyle modifications, and regular medical check-ups to prevent or minimize these complications.
Sexual Dysfunction
Diabetic neuropathy can also contribute to sexual dysfunction in both men and women. Nerve damage can affect sexual response, leading to symptoms such as erectile dysfunction in men and decreased arousal or reduced lubrication in women. Open communication with a healthcare professional is essential to address these concerns and explore potential treatment options or strategies to improve sexual function and intimacy.
Gastroparesis
Gastroparesis, a condition in which the stomach takes longer than usual to empty its contents, can be a complication of diabetic neuropathy affecting the nerves controlling digestion. This can lead to symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, bloating, and lack of appetite. Managing blood sugar levels, dietary modifications, and medications can help alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications associated with gastroparesis.
This image is property of www.eastcoastpodiatry.sg.
Future Research and Developments
Advancements in Treatment Options
Ongoing research and advancements in treatment options offer hope for individuals with diabetic neuropathy. Scientists and healthcare professionals are continually exploring new medications, nerve stimulation techniques, and targeted therapies to manage the symptoms and slow down the progression of this condition. Collaborative efforts between researchers, pharmaceutical companies, and healthcare providers pave the way for improved treatment strategies and better outcomes for individuals with diabetic neuropathy.
Regenerative Medicine
Regenerative medicine holds promise in the field of diabetic neuropathy. Stem cell-based therapies and tissue engineering techniques aim to develop new nerve tissues and restore damaged nerve function. Regenerative medicine approaches may offer potential therapies for promoting nerve regeneration and reversing some of the complications associated with diabetic neuropathy. Although still in the experimental stages, these advancements provide hope for future treatment options.
Gene Therapy
Gene therapy, a growing field of research and development, holds the potential to address the underlying causes of diabetic neuropathy. By targeting the specific genes or genetic mutations associated with nerve damage, scientists aim to develop advanced treatments that can repair or prevent nerve damage in individuals with diabetes. The potential of gene therapy in managing diabetic neuropathy shows promise but requires further research and clinical trials.
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology, the manipulation of matter at the atomic and molecular scale, offers exciting possibilities for diabetic neuropathy treatment. Nanoparticles, when engineered appropriately, can deliver medications or therapeutic agents directly to damaged nerves. This targeted approach may enhance drug effectiveness and minimize side effects. The use of nanotechnology in developing advanced therapeutic approaches for diabetic neuropathy is an area of active research.
Conclusion
Raising awareness of diabetic neuropathy and its potential consequences is vital for individuals with diabetes and the healthcare community. Understanding the types, causes, and symptoms of diabetic neuropathy empowers individuals to take proactive steps in prevention and early intervention. By maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, engaging in regular exercise and physical activity, following a healthy diet, and prioritizing foot care, individuals can reduce their risk of developing diabetic neuropathy and its associated complications. Regular medical check-ups, proper management of pain and other symptoms, and emotional support are essential for individuals living with diabetic neuropathy. With ongoing research and advancements in treatment options, there is hope for improved therapies and better outcomes for those affected by diabetic neuropathy.
Related posts:
 Understanding the Impact of Diabetes on Pregnancy: Mother and Child Concerns
Understanding the Impact of Diabetes on Pregnancy: Mother and Child Concerns
 Tips for Managing Blood Sugar Levels Effectively
Tips for Managing Blood Sugar Levels Effectively
 Long-Term Health Concerns for Women with Diabetes
Long-Term Health Concerns for Women with Diabetes
 Balancing Diabetes Management and Enjoyment through a Healthy Diet
Balancing Diabetes Management and Enjoyment through a Healthy Diet
 Coping with the Emotional Challenges of Living with Diabetes
Coping with the Emotional Challenges of Living with Diabetes
 The Cost of Diabetes Medication: A Barrier for Women
The Cost of Diabetes Medication: A Barrier for Women










No comment yet, add your voice below!