Losing weight can be a challenging endeavor, but have you ever wondered why it seems easier for some people than others? In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of genetics and metabolism and their profound impact on our weight loss journeys. By understanding these intricate factors, we can gain valuable insights into how our bodies respond to various diets, exercise regimens, and lifestyle changes. So, get ready to unravel the secrets behind why shedding those extra pounds may be more complex than meets the eye.

This image is property of images.pexels.com.
In This Article
ToggleGenetics and Weight Loss
Introduction to Genetics
When it comes to weight loss, many factors come into play, including genetics. Genetics refers to the study of genes and how they are inherited from our parents. These genes play a significant role in determining various traits, including our body weight and metabolism. Understanding the impact of genetics on weight loss can help us develop personalized strategies that are tailored to our unique genetic makeup.
Understanding Genetic Factors in Weight Loss
Genetic factors can significantly influence our ability to lose weight. Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to obesity, making it more challenging for them to shed excess pounds. Additionally, genetic variations can affect how our bodies process and store fat, as well as how efficiently we burn calories. By understanding these genetic factors, we can better comprehend why some individuals may struggle more than others when it comes to weight loss.
Impact of Genes on Metabolism
Metabolism refers to the chemical processes that occur within our bodies to convert food into energy. Our metabolism plays a vital role in weight loss, as it determines how efficiently we burn calories. Genetics can impact our metabolism in several ways. Certain genetic variations can cause a slower metabolism, making it easier for weight to be gained and harder for weight to be lost. On the other hand, some individuals may have a faster metabolism, making it easier for them to maintain a healthy weight.
Genetic Predisposition to Obesity
Research has shown that genetics can contribute to a predisposition to obesity. This means that some individuals may have a higher risk of becoming overweight or obese due to their genetic makeup. Several genes have been identified that play a role in regulating appetite, fat storage, and metabolism. For example, the FTO gene has been associated with an increased risk of obesity. By understanding these genetic predispositions, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their weight more effectively.
Influence of Family History on Weight Loss
Family history can also play a significant role in weight loss. Studies have shown that individuals with a family history of obesity are more likely to struggle with weight management themselves. This can be attributed to a combination of genetic factors and shared lifestyle habits within the family. By recognizing the influence of family history, individuals can be more mindful of their genetic predispositions and take steps to adopt healthier lifestyle habits.
Metabolism and Weight Loss
Introduction to Metabolism
Metabolism is the process by which our bodies convert the food we eat into energy. It involves various chemical reactions that occur within our cells. Our metabolism is responsible for maintaining essential bodily functions, such as breathing, circulating blood, and repairing cells. Understanding metabolism is crucial in understanding how our bodies burn calories and how we can optimize it for weight loss.
Types of Metabolism
There are two main types of metabolism: catabolism and anabolism. Catabolism refers to the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy in the process. Anabolism, on the other hand, is the process of building complex molecules from simpler ones, requiring energy. Both types of metabolism play a role in our overall energy balance and weight management.
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
The basal metabolic rate (BMR) is a measure of the calories our bodies burn at rest. It represents the minimum amount of energy needed to maintain bodily functions such as breathing, circulating blood, and regulating body temperature. Several factors influence our BMR, including age, gender, body composition, and genetics. Understanding our BMR can help us determine our daily calorie needs and set realistic weight loss goals.
Thermic Effect of Food (TEF)
The thermic effect of food (TEF) refers to the energy expenditure required for the digestion, absorption, and utilization of the nutrients in the food we eat. Different foods have varying TEFs, with protein having the highest thermic effect. By consuming foods that have a higher TEF, we can potentially increase our calorie burn and support weight loss efforts.
Physical Activity and Its Effect on Metabolism
Physical activity plays a crucial role in weight loss by increasing our overall energy expenditure. Engaging in regular exercise not only burns calories during the activity but also increases our metabolic rate and calorie burn even at rest. Strength training, in particular, can help build muscle, which is more metabolically active than fat, leading to a higher overall metabolic rate.
Genetic Factors affecting Weight Loss
Role of FTO Gene
The FTO gene, also known as the “fat mass and obesity-associated gene,” has been extensively studied in relation to weight loss. Variations in the FTO gene have been associated with a higher risk of obesity and difficulty in losing weight. This gene is believed to influence appetite regulation and food intake, making it harder for individuals with certain FTO gene variations to control their eating habits and manage their weight.
Leptin and Leptin Resistance
Leptin is a hormone produced by fat cells that plays a crucial role in regulating appetite and metabolism. It sends signals to the brain to reduce hunger and increase energy expenditure. However, in some individuals, a condition called leptin resistance can occur, where the brain becomes less responsive to the signals sent by leptin. This can lead to an increased appetite and difficulty in achieving weight loss.
Ghrelin and Its Effect on Appetite
Ghrelin is another hormone that plays a role in appetite regulation. It is often referred to as the “hunger hormone” as it increases hunger and stimulates food intake. Genetic variations can impact ghrelin production and sensitivity, leading to differences in appetite and food cravings. Understanding these genetic factors can help individuals develop strategies to manage their appetite and make healthier food choices.
Insulin Resistance and Weight Loss Challenges
Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. Insulin resistance occurs when cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin, leading to chronically high blood sugar levels. This can contribute to weight gain and make it more challenging to lose weight. Genetic variations can influence insulin sensitivity and insulin resistance, potentially impacting weight loss efforts.
Genetic Variations in Fat Storage and Burning
Genetic variations can also impact how our bodies store and burn fat. Certain genes regulate fat metabolism, affecting how efficiently our bodies break down and utilize stored fat for energy. Variations in these genes can influence an individual’s ability to lose weight and maintain a healthy body composition. Understanding these genetic variations can help tailor weight loss strategies to optimize fat burning and storage.
Impact of Metabolism on Weight Loss
Slow Metabolism and Weight Gain
A slow metabolism can make it easier for weight to be gained and harder for weight to be lost. This can be attributed to several factors, including genetics, age, and hormonal changes. Individuals with a slower metabolism may need to be more mindful of their calorie intake and engage in regular physical activity to support weight loss efforts.
Factors Influencing Basal Metabolic Rate
Several factors can influence our Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR). Age, gender, body composition, and genetics all play a role in determining our BMR. As we age, our BMR naturally decreases, making weight management more challenging. Men generally have a higher BMR than women, primarily due to differences in body composition, such as muscle mass. Understanding these factors can help individuals adjust their lifestyle habits and set realistic weight loss goals.
Thermogenesis and Its Role in Weight Loss
Thermogenesis refers to the production of heat within our bodies. It is closely linked to our metabolic rate and can impact our ability to lose weight. Certain foods, such as those rich in protein, have a thermogenic effect, increasing our energy expenditure and supporting weight loss. Additionally, activities such as cold exposure and exercise can stimulate thermogenesis and boost calorie burn.
Muscle Mass and Metabolism
Muscle mass plays a critical role in our metabolism. Muscle tissue is more metabolically active than fat tissue, meaning it burns more calories at rest. Individuals with higher muscle mass tend to have a faster metabolism, making it easier for them to maintain a healthy weight. Incorporating strength training exercises into a weight loss routine can help preserve and build muscle mass, supporting long-term weight management.
Metabolic Adaptation to Caloric Restriction
When we restrict our calorie intake for weight loss, our bodies can undergo metabolic adaptation. This refers to the physiological changes that occur in response to reduced calorie intake, including a decrease in metabolic rate. Our bodies are designed to adapt to periods of food scarcity, conserving energy and slowing down our metabolism to preserve fat stores. Understanding this metabolic adaptation can help individuals develop strategies to prevent weight loss plateaus and maintain long-term weight loss.

This image is property of images.pexels.com.
Interplay between Genetics and Metabolism
How Genetics Influence Metabolism
Genetics can influence our metabolism by regulating various factors, including hormone production, enzyme activity, and energy expenditure. Genetic variations can impact the functioning of genes involved in metabolism, leading to differences in how our bodies process and utilize nutrients. By understanding our genetic predispositions, we can better tailor our lifestyle habits and diet to optimize our metabolism for weight loss.
Genetic Factors Affecting Macronutrient Metabolism
Macronutrients, such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, play a vital role in our metabolism. Genetic variations can influence how our bodies metabolize and respond to different macronutrients, affecting our energy balance and weight management. For example, some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to efficiently process carbohydrates, making them more prone to weight gain from high-carbohydrate diets.
Genetic Variations in Energy Expenditure
Genetic variations can also impact our energy expenditure, or the number of calories we burn in a day. Certain genes regulate our basal metabolic rate and physical activity levels, affecting our overall energy expenditure. By understanding these genetic variations, individuals can tailor their exercise routines and lifestyle habits to optimize their calorie burn and support weight loss efforts.
Common Genetic Markers and Weight Loss
Advancements in genetic research have identified several common genetic markers associated with weight loss. These markers can provide valuable insights into an individual’s genetic predispositions and potential challenges when it comes to weight loss. By understanding these genetic markers, individuals can develop personalized weight loss strategies that take into account their unique genetic makeup.
Understanding Epigenetics in Relation to Weight Loss
Epigenetics refers to the study of heritable changes in gene expression that do not involve changes in the underlying DNA sequence. It involves modifications to the DNA molecules or the proteins associated with DNA that can alter how genes are turned on or off. Epigenetic changes can be influenced by various factors, including diet, lifestyle, and environmental factors, and can impact our metabolism and weight loss efforts. Understanding epigenetics can help individuals make informed choices that can positively influence gene expression and support weight management.
Tailoring Weight Loss Strategies based on Genetics
Using Genetic Testing for Personalized Plans
Genetic testing has become increasingly popular in the field of weight loss and wellness. These tests analyze an individual’s DNA to identify specific genetic variations associated with weight management. By understanding their unique genetic makeup, individuals can receive personalized recommendations for diet, exercise, and lifestyle modifications to optimize their weight loss journey.
Genetic Counseling and Weight Management
Genetic counseling can be a valuable resource for individuals seeking guidance in their weight loss efforts. Genetic counselors are trained professionals who specialize in interpreting and explaining genetic test results. They can provide personalized advice and support based on an individual’s genetic predispositions and help them navigate the complexities of weight management.
Adapting Exercise Regimens for Genetic Variations
Genetic variations can impact how our bodies respond to different types of exercise. Some individuals may be more genetically suited for endurance-based activities, while others may excel in strength training. Understanding our genetic predispositions can help us tailor our exercise regimens to maximize results and improve compliance to achieve long-term weight loss success.
Matching Diet Plans to Genetic Profiles
Our genetic makeup can impact how our bodies process and respond to different nutrients, such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. By understanding our genetic profiles, we can identify specific dietary approaches that may be more effective for weight loss. For example, individuals with a genetic predisposition to insulin resistance may benefit from a lower carbohydrate diet, while those with certain fat metabolism variations may benefit from a higher fat intake.
Psychological Support in Genetic-based Weight Loss
Weight loss can be a challenging journey, especially when genetic factors are involved. Psychological support is crucial for individuals navigating the complexities of weight loss based on their genetic predispositions. Counseling, support groups, and other mental health resources can help individuals build resilience, develop coping strategies, and maintain motivation throughout their weight loss journey.

This image is property of images.pexels.com.
Factors Beyond Genetics and Metabolism in Weight Loss
Lifestyle and Behavioral Factors
While genetics and metabolism play significant roles in weight loss, lifestyle and behavioral factors also have a significant impact. Factors such as diet quality, portion control, physical activity levels, stress management, and sleep patterns all play a crucial role in weight management. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits and making sustainable behavior changes, individuals can optimize their weight loss efforts.
Stress and Its Impact on Weight
Chronic stress can have a significant impact on weight management. When we are under stress, our bodies release cortisol, a hormone that can increase appetite and promote weight gain, especially around the abdominal area. Additionally, individuals may turn to food as a way to cope with stress, leading to emotional eating and weight gain. Implementing stress management techniques, such as exercise, mindfulness, and relaxation techniques, can help individuals better manage their weight.
Sleep and Weight Loss
Sleep plays a vital role in weight management. Lack of sleep can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to increased appetite, decreased satiety, and alterations in metabolism. Sleep deprivation is also associated with decreased motivation to engage in physical activity and make healthier food choices. Prioritizing sleep hygiene and aiming for adequate sleep can support weight loss efforts.
Role of Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome, which refers to the diverse community of microbes in our intestines, has emerged as a significant player in weight management. Research has shown that the composition and function of the gut microbiome can impact our metabolism, appetite regulation, and fat storage. By prioritizing a diet rich in high-fiber, plant-based foods, individuals can nurture a healthy gut microbiome and support their weight loss goals.
Environmental Factors Influencing Weight
Environmental factors can also influence weight management. Access to healthy food options, built environments that promote physical activity, and social and cultural influences all play a role in shaping our lifestyle habits and choices. By creating supportive environments that promote healthy living and weight management, individuals can overcome potential barriers and increase their chances of success.
Challenges in Weight Loss with Genetic and Metabolic Factors
Difficulty in Sustained Weight Loss
Sustained weight loss can be challenging for individuals with genetic and metabolic factors influencing their weight. The body’s natural response to reduced calorie intake and weight loss is to conserve energy and slow down the metabolism, making it harder to maintain weight loss long-term. Developing strategies to overcome these challenges, such as adopting sustainable lifestyle changes and seeking ongoing support, can help individuals achieve and maintain their weight loss goals.
Plateaus and Weight Regain
Weight loss plateaus, where progress stalls despite consistent efforts, can be discouraging. Genetic and metabolic factors can contribute to weight loss plateaus, as our bodies adapt to calorie restriction and changes in physical activity levels. Additionally, weight regain can occur if individuals revert to old habits or struggle with their genetic predispositions. Implementing strategies such as varying exercise routines, adjusting calorie intake, and regularly reassessing goals can help break through plateaus and prevent weight regain.
Genetic Resistance to Weight Loss
Some individuals may experience genetic resistance to weight loss, where their bodies are inherently more resistant to the changes required for weight management. This resistance can be due to genetic variations that impact appetite control, fat metabolism, and insulin sensitivity. While genetic resistance to weight loss can be discouraging, it is essential to focus on overall health improvements rather than solely on the number on the scale.
Metabolic Adaptation and Weight Loss Plateaus
Metabolic adaptation is a significant challenge individuals face during weight loss. As the body adapts to reduced calorie intake, metabolic rate decreases, making weight loss more difficult. This metabolic adaptation can lead to weight loss plateaus, where individuals experience a stall in progress despite consistent efforts. Remaining patient, adjusting calorie intake, and incorporating exercise and strength training can help overcome metabolic adaptation and break through plateaus.
Managing Expectations in Genetic-based Weight Loss
Managing expectations is crucial when it comes to weight loss, especially when genetic and metabolic factors are involved. It is essential to recognize that weight loss journeys can vary significantly from person to person, and progress may be slower or more challenging for some individuals. Setting realistic goals and focusing on overall health improvements rather than solely on weight can help individuals stay motivated and maintain a positive mindset throughout their weight loss journey.
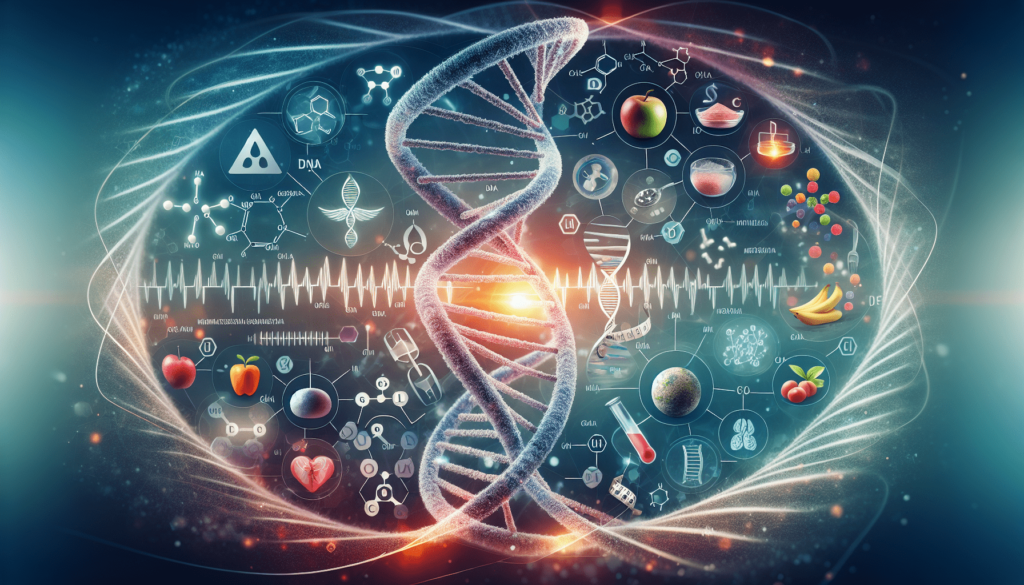

Emerging Research and Technologies
Epigenetic Modifications and Weight Loss
Emerging research suggests that epigenetic modifications may play a role in weight loss and metabolism. Epigenetic changes can be influenced by various factors, including diet, lifestyle, and environmental factors, and may impact gene expression related to metabolism and weight management. Understanding these epigenetic modifications can provide valuable insights into personalized weight loss strategies and open up new avenues for research and development in the field.
Pharmacogenomics in Weight Management
Pharmacogenomics is an emerging field that explores how genetic variations can influence an individual’s response to medications. In the context of weight management, pharmacogenomics can help identify the most effective medications or weight loss interventions based on an individual’s genetic makeup. This personalized approach can improve treatment outcomes and optimize weight loss efforts.
Gene Therapies for Metabolic Disorders
Advancements in gene therapy offer exciting possibilities for the treatment of metabolic disorders. Gene therapy involves introducing genetic material into cells to address specific genetic abnormalities. While still in the early stages of development, gene therapies hold promise for treating metabolic disorders such as obesity by targeting specific genes related to fat metabolism and appetite regulation. Continued research in this field may revolutionize weight management strategies in the future.
Advances in Metabolic Rate Assessment
Accurately assessing metabolic rate is crucial for effective weight management. Advancements in technology have led to the development of various methods for measuring metabolic rate, ranging from simple equations based on age, gender, and weight to more advanced techniques such as indirect calorimetry and metabolic carts. These advancements allow for more precise and personalized approaches to weight loss, optimizing calorie intake and expenditure.
Precision Nutrition and Personalized Dietary Recommendations
Precision nutrition refers to the practice of tailoring dietary recommendations based on an individual’s unique genetic and metabolic profile. By analyzing an individual’s genetic makeup and metabolic markers, precision nutrition can provide personalized dietary recommendations that optimize weight loss and overall health. This approach takes into account individual differences in nutrient metabolism and absorption, allowing for a more individualized and effective weight loss strategy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the interplay between genetics and metabolism has a profound impact on weight loss. Understanding the influence of genetics and metabolism on weight management can help individuals develop personalized strategies that work harmoniously with their unique genetic makeup. By recognizing the interplay between genetics, metabolism, lifestyle factors, and environmental influences, individuals can achieve effective and sustainable weight management. Continued research and development in the field are essential for furthering our understanding and providing innovative approaches to personalized weight loss. Building a holistic understanding of the complex factors involved in weight management is key to successful and individualized weight loss strategies.
Related posts:
 Understanding the Impact of Diabetes on Pregnancy: Mother and Child Concerns
Understanding the Impact of Diabetes on Pregnancy: Mother and Child Concerns
 Extreme Weight Loss Pills for Men and Women: Hydroxycut Hardcore Elite – Maximum Strength Weight Loss Supplement with Energy Boost and Metabolism Booster – 110 Capsules offered in various package sizes
Extreme Weight Loss Pills for Men and Women: Hydroxycut Hardcore Elite – Maximum Strength Weight Loss Supplement with Energy Boost and Metabolism Booster – 110 Capsules offered in various package sizes
 Maintain a Healthy Metabolism with Culturelle Healthy Metabolism Supplement, 30 Capsules
Maintain a Healthy Metabolism with Culturelle Healthy Metabolism Supplement, 30 Capsules
 The Impact of Food Deserts on the Availability of Healthy Food Options
The Impact of Food Deserts on the Availability of Healthy Food Options
 Understanding the Relationship Between Weight and Self-Esteem
Understanding the Relationship Between Weight and Self-Esteem
 Understanding the Link Between Weight and Fertility
Understanding the Link Between Weight and Fertility











No comment yet, add your voice below!